
Keeping your blood pressure in healthy range is a key to overall wellness. High blood pressure, or hypertension, can lead to serious issues like heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to keep your blood pressure under control. In this detailed guide, we’ll share expert advice from top cardiologists on how to lower blood pressure and boost heart health.
Understanding Blood Pressure and Its Importance
Blood pressure measures the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries as it flows through your body. It’s recorded with two numbers: systolic pressure (when your heart beats) and diastolic pressure (when your heart rests between beats). High blood pressure, or hypertension, occurs when this force is consistently too high, putting extra strain on your heart and arteries.
The Impact of High Blood Pressure on Heart Health
High blood pressure is often called the “silent killer” because it typically has no symptoms but can cause significant damage over time. If left unchecked, it can lead to heart disease, heart failure, and other serious cardiovascular issues. The constant high pressure can damage the delicate lining of the arteries, making them more prone to plaque buildup. This narrows the arteries, reduces blood flow, and raises the risk of a heart attack or stroke.
Lifestyle Changes to Lower Blood Pressure

Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of high blood pressure. Losing extra pounds can significantly lower your blood pressure and improve heart health. Aim for a body mass index (BMI) in the healthy range.
Reduce Sodium Intake
Too much sodium can lead to high blood pressure. Experts recommend keeping sodium intake below 2,300 milligrams per day. To do this, cut back on processed foods, canned soups, and fast food.
Increase Potassium-Rich Foods
Potassium helps balance the effects of sodium and can help lower blood pressure. Add potassium-rich foods like bananas, oranges, spinach, and avocados to your diet.
The Role of a Healthy Diet in Managing Blood Pressure

Follow the DASH Diet
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is specifically designed to lower blood pressure. It focuses on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy while limiting saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
Increase Fiber Intake
Eating enough dietary fiber can help lower blood pressure. Include fiber-rich foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes in your meals.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption
Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure. It’s important to drink in moderation. Experts suggest no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
Regular Physical Activity for Maintaining Heart Health

Engage in Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercises, like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, can help lower blood pressure. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Incorporate Strength Training
Strength training exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, can also positively impact blood pressure. Aim for at least two days of strength training per week, focusing on major muscle groups.
Stay Active Throughout the Day
In addition to structured exercise, find ways to stay active all day. Take the stairs instead of the elevator, walk or bike to work if possible, and break up long periods of sitting with short activity bursts.
Stress Management Techniques to Reduce Blood Pressure

Practice Relaxation Techniques
Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and lower blood pressure. Find a relaxation method that works for you and make it a part of your daily routine.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Exercise benefits your physical health and helps reduce stress. Regular physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters.
Get Enough Sleep
Lack of sleep or poor sleep quality can increase blood pressure. Aim for seven to eight hours of quality sleep each night to support heart health.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups and Medication Adherence

Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring blood pressure and overall heart health. If you’re prescribed medication for blood pressure, it’s crucial to follow your treatment plan.
Monitor Blood Pressure at Home
Use a reliable blood pressure monitor to check your blood pressure at home regularly. Record the readings and share them with your doctor during visits.
Take Prescribed Medication as Directed
If your doctor prescribes medication to manage your blood pressure, take it as directed. Don’t skip doses or stop the medication without consulting your doctor.
Attend Regular Check-Ups
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your blood pressure and discuss any health concerns. These visits help your doctor adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Lowering Blood Pressure

Along with lifestyle changes and medication, some natural remedies and supplements may positively affect blood pressure. Always consult your doctor before adding new supplements to your routine.
Garlic
Garlic supplements might help lower blood pressure, though results can vary. Discuss with your doctor if garlic supplements are a good option for you.
Fish Oil
Omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil supplements have been linked to lower blood pressure. However, talk to your doctor to determine the right dosage and ensure it’s safe for you.
Hibiscus Tea
Some studies suggest that hibiscus tea may help lower blood pressure. More research is needed to fully understand its benefits and any potential interactions with medications.
The Benefits of Quitting Smoking and Reducing Alcohol Consumption

Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are harmful to heart health and can contribute to high blood pressure. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake can significantly improve your heart health.
Quit Smoking
Smoking damages blood vessels and raises blood pressure. If you smoke, seek support and resources to quit. Your doctor can provide guidance and recommend strategies to help you quit successfully.
Reduce Alcohol Consumption
Limiting alcohol intake can help lower blood pressure and decrease the risk of heart-related complications. If you need help reducing your alcohol consumption, reach out to healthcare professionals or support groups.
Support and Resources for Managing Blood Pressure and Improving Heart Health

Managing blood pressure and improving heart health can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. Various resources and support systems are available to assist you.
Local Healthcare Providers
Contact your local healthcare providers for personalized guidance and support. They can help you create a plan to manage your blood pressure and improve your heart health.
Online Communities
Joining online communities focused on heart health can provide a sense of community and support. Connect with others on a similar journey and exchange helpful tips and experiences.
Educational Materials
Stay informed about the latest research and recommendations on blood pressure management and heart health. Educate yourself through reliable sources, such as medical websites, books, and reputable health organizations.
FAQs

Can anxiety cause high blood pressure?
Yes, anxiety can cause temporary spikes in blood pressure. Chronic anxiety may contribute to long-term high blood pressure.
Does dehydration cause high blood pressure?
Dehydration can lead to low blood pressure, but over time, it can also contribute to high blood pressure due to the body’s compensatory mechanisms.
Does drinking water lower blood pressure?
Staying well-hydrated can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels. However, it is not a cure for high blood pressure.
Does fasting lower blood pressure?
Fasting can lead to temporary drops in blood pressure, but its long-term effects on blood pressure are still being studied.
Can pain cause high blood pressure?
Yes, acute pain can cause temporary increases in blood pressure due to the body’s stress response.
Can lack of sleep cause high blood pressure?
Chronic sleep deprivation can contribute to high blood pressure and other cardiovascular issues.
Does blood pressure rise after eating?
Yes, blood pressure can temporarily rise after eating, especially large meals.
When is blood pressure high enough to go to the hospital?
Seek medical attention if your blood pressure readings are consistently above 180/120 mmHg, or if you experience symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or severe headache.
What blood pressure is considered high?
Blood pressure readings of 140/90 mmHg or higher are considered high.
Causes of blood pressure
Various factors, including genetics, poor diet, lack of exercise, and stress can cause high blood pressure.
Blood pressure chart by age and gender
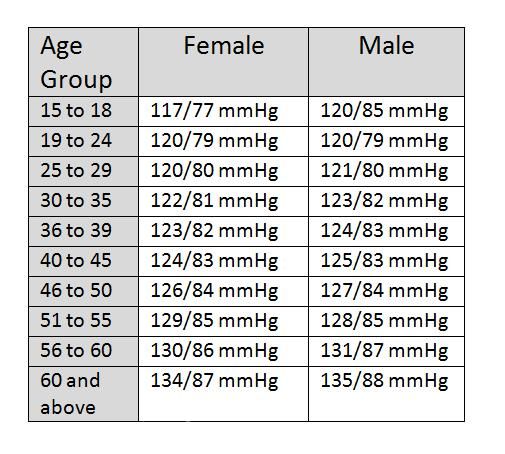
To sum up, taking proactive steps to lower your blood pressure and improve your heart health is essential for overall well-being. By following these expert tips from top cardiologists, you can positively impact your cardiovascular health. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making significant lifestyle changes or adding new supplements. Take charge of your health today and make your heart a priority.


Very interesting topic, thank you for posting.Blog money
Thank you very much.